.
Welcome to Hydrogen Energy Basics
Hydrogen energy, often hailed as the fuel of the future, is a promising alternative to traditional fossil fuels. As the world seeks sustainable energy solutions to combat climate change and reduce carbon emissions, hydrogen emerges as a key player in the energy transition. Understanding the basics of hydrogen energy and its various forms is crucial in realizing its potential to revolutionize our energy systems.
What is Hydrogen Energy?
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe, and it holds immense potential as a clean and renewable energy carrier. When used in fuel cells or combustion engines, hydrogen produces electricity, with water and heat as the only byproducts, making it a zero-emission energy source.
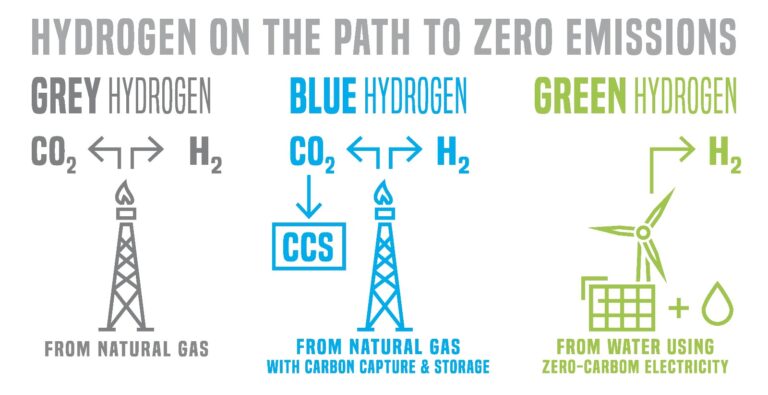
Main 3 Types of Hydrogen Energy
- Grey Hydrogen: Grey hydrogen is produced from fossil fuels, primarily natural gas, through a process called steam methane reforming (SMR). While it is currently the most common method of hydrogen production, it emits significant amounts of carbon dioxide, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Blue Hydrogen: Blue hydrogen is similar to grey hydrogen in production methods, but with one crucial difference: carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology is employed to capture and store the carbon emissions generated during the production process. This significantly reduces the carbon footprint of hydrogen production, making it a transitional solution towards greener hydrogen.
- Green Hydrogen: Green hydrogen is produced through the process of electrolysis, where an electric current splits water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. When powered by renewable energy sources such as solar or wind, green hydrogen production becomes entirely emissions-free, offering a truly sustainable energy solution.
